Worried about unseen damage ruining your products? Static discharge is a silent killer in many industries, causing costly failures. Let’s look at why controlling it is vital.
Static protection prevents electrostatic discharge (ESD). ESD can destroy sensitive electronics, ignite flammable materials, and cause equipment malfunctions. Implementing proper controls protects products, ensures safety, and saves money by reducing failures and downtime. It’s essential for quality and reliability.
That little zap might seem harmless, but the consequences can be huge for businesses like yours and mine. I’ve seen firsthand how overlooking this can lead to disaster. So, let’s dig deeper into what this static menace really is and why it demands our attention.
What Exactly Is Static Discharge and Why Should I Care?
Ever felt a shock touching a doorknob? That’s static discharge. In industry, these tiny sparks can cause massive, expensive problems you might not even see happening.
Static discharge, or ESD, is the sudden flow of electricity between two charged objects. You should care because it can instantly destroy sensitive electronic components, corrupt data, or even ignite flammable vapors, leading to significant financial loss and safety hazards in your workplace.
Okay, let’s break this down. Static electricity builds up when different materials rub together or separate. Think about walking across a carpet – your body collects charge. This is called the triboelectric effect. Some materials give up electrons easily, others grab them. When enough charge builds up, it wants to jump to something with less charge – that’s the discharge, the zap or ESD.
How Static Builds Up
It happens everywhere, all the time. Simple actions like:
- Walking across certain floors.
- Unrolling tape.
- Sliding components in a bag.
- Even airflow over a surface.
Insulating materials hold this charge, making the problem worse until a discharge path appears, often through a sensitive component or person. I remember visiting a facility where operators shuffling plastic bins were unknowingly creating huge static fields near sensitive assemblies.
The Dangers of ESD
Why is this tiny spark such a big deal?
- Component Damage: Modern electronics are incredibly sensitive. A discharge invisible to us can fry them instantly (catastrophic failure) or weaken them so they fail later (latent failure). This hurts product quality and reliability. I once saw a whole batch of boards fail testing because of poor handling procedures that ignored static risks.
- Fire/Explosion: In areas with flammable solvents, gases, or dust, an ESD spark is a dangerous ignition source. Safety is paramount here.
- Equipment Malfunction: ESD can cause machines to lock up, reset, or behave unpredictably, leading to downtime and production headaches.
- Data Corruption: Static fields can sometimes affect magnetic storage media.
Understanding these risks is the first step to controlling them. It’s not just about preventing shocks; it’s about protecting the core of your business operations and ensuring product integrity from start to finish.
Which Industries Absolutely Need Strong ESD Controls?
Think your industry is safe from static? Many sectors face hidden ESD risks daily. Ignoring them can lead to costly failures and safety incidents you didn’t expect.
Industries handling sensitive electronics (manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, medical devices, data centers) are prime candidates. Also, sectors using flammable materials (chemical, pharmaceutical, oil & gas) need strict ESD controls to prevent ignition risks. Basically, anywhere sensitive components or flammable substances exist.

It’s easy to think ESD is just an electronics problem, but the reach is wider than you might expect. Certain industries are definitely more vulnerable, and ignoring ESD can have severe consequences. I’ve worked with clients across several of these fields and seen the impact firsthand.
Electronics and Manufacturing
This is ground zero for ESD concerns. Anyone making, handling, testing, or repairing circuit boards, semiconductors, or electronic devices needs robust ESD protection. Think about:
- Consumer electronics assembly
- Telecommunications equipment production
- Computer and peripheral manufacturing
The components are just too sensitive to stray voltage, and failures here mean direct hits to yield and profit.
Hazardous Environments
Anywhere you have flammable liquids, gases, powders, or dusts, ESD is a serious fire or explosion risk. This includes:
- Chemical processing plants
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities
- Oil and gas refineries and platforms
- Paint shops and finishing lines
- Grain handling and storage silos
Here, safety is the absolute top priority, and ESD control is a critical, often regulated, part of that safety system.
Other Sensitive Areas
Don’t forget these sectors where reliability is key:
- Aerospace & Defense: Complex, mission-critical electronics demand the highest reliability. Failure isn’t an option.
- Automotive: Modern cars are packed with sensitive electronic control units (ECUs) and sensors.
- Medical Devices: Device reliability can be a matter of life and death for patients.
- Data Centers: Protecting servers, storage, and ensuring data integrity is crucial for uptime and business continuity.
Here’s a simple table highlighting the main risk:
| Industry | Main ESD Risk |
|---|---|
| Electronics Mfg. | Component Damage |
| Chemical/Oil&Gas | Fire/Explosion |
| Aerospace/Defense | Reliability/Safety |
| Automotive | Reliability |
| Medical Devices | Reliability/Safety |
| Data Centers | Damage/Downtime |
If your industry involves any of these activities or environments, you definitely need a solid ESD control plan.
How Can I Effectively Implement ESD Protection in My Workplace?
Feeling overwhelmed by ESD protection options? Implementing controls seems complex and costly. But ignoring it costs more. Let’s simplify the essential steps you can take.
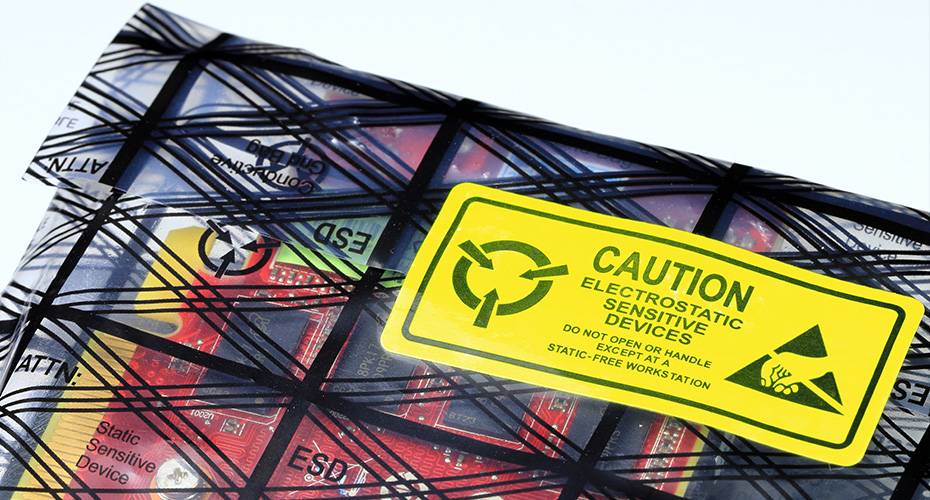
Effective ESD protection involves creating an Electrostatic Protected Area (EPA). Key elements include grounding personnel (wrist straps), using ESD-safe workstations (mats, flooring), proper handling procedures, ESD-safe packaging, and controlling humidity. Regular training and audits are also crucial.

So, how do we actually stop ESD? It’s about creating a safe zone and using the right tools and habits. It doesn’t have to be overly complicated if you focus on the fundamentals. I always advise starting with these core areas.
Grounding is Key
The most basic principle is keeping everything – people, surfaces, equipment – at the same electrical potential, usually ground potential. If there’s no difference in charge level, there’s no sudden discharge.
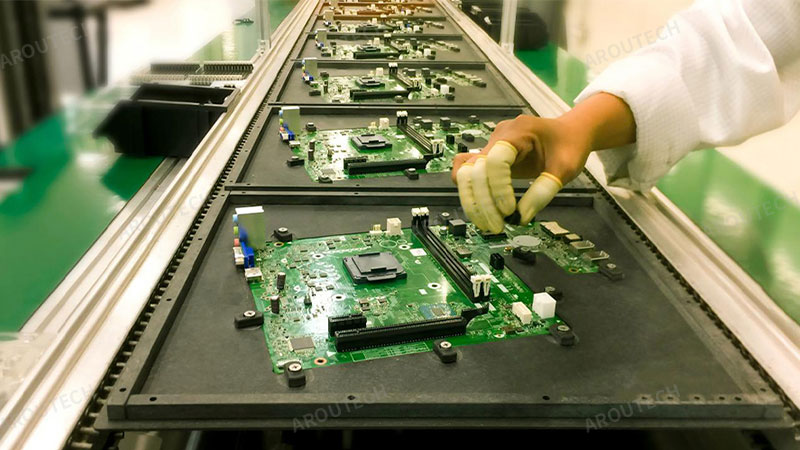
- Ground People: Anyone handling sensitive items must be connected to ground. The most common way is using a wrist strap connected via a cord to a common ground point. In areas where mobility is needed, ESD-safe footwear used with conductive or dissipative flooring systems achieves the same goal.
- Ground Work Areas: Benchtops where sensitive items are handled need ESD-safe mats. These mats are connected to the same common ground point, allowing any charge on items placed on them to drain away safely.
- Ground Tools & Equipment: Metal tools and equipment chassis should also be properly grounded.
Creating an EPA (Electrostatic Protected Area)
This is your designated safe zone. Inside an EPA, all surfaces, objects, and people are kept at the same electrical potential. An EPA typically includes:
- Grounded worksurface mats.
- Personnel grounding systems (wrist straps or footwear/flooring).
- ESD-safe flooring or floor mats.
- Clear signs marking the EPA boundaries.
- Sometimes, ionizers are needed. These devices blow ionized air to neutralize static charges on essential insulators (like some plastics) that cannot be grounded.
Handling and Training
Having the right gear isn’t enough; people need the right habits and knowledge.
- Procedures: Always use ESD-safe bags, bins, or containers for storing and transporting sensitive items outside the EPA. Handle components by their edges, not by their leads.
- Training: Everyone working in or near an EPA needs regular training. They must understand why ESD control is important and how to follow the procedures correctly. I’ve seen training programs dramatically cut down on previously unexplained failures.
- Checks & Audits: Regularly test wrist straps, footwear, mats, and ground connections using appropriate meters to ensure they are functioning correctly. This verification step is vital.
Think of it like building layers of defence against static. Each element plays a part in creating a safe environment for sensitive components.
What Are the Real Benefits of Investing in ESD Safety?
Think ESD protection is just another expense? The cost of not controlling static can be far higher. Hidden failures, low yields, and safety risks eat into profits silently.
Investing in ESD safety brings huge benefits: improved product quality and reliability, reduced manufacturing costs (less rework/scrap), enhanced workplace safety (preventing fires/shocks), increased customer satisfaction, and compliance with industry standards. It protects your bottom line and reputation.

Spending money on wrist straps, mats, and training might feel like just another operational cost. But trust me, based on what I’ve seen across many companies, the return on investment for proper ESD control is significant and multifaceted. It’s not just about preventing zaps; it’s about improving the business.
Better Products, Lower Costs
This is often the most direct and measurable benefit.
- Higher Manufacturing Yields: Fewer components getting damaged during assembly, testing, and handling means more good products successfully make it through the production line on the first pass.
- Less Rework & Scrap: Catching and preventing ESD damage saves the significant time, labor, and material costs associated with fixing failed units or discarding them entirely.
- Improved Product Reliability: Products are far less likely to fail prematurely out in the field due to latent ESD damage that weakened components during production. This translates directly to fewer warranty claims, reduced service costs, and happier customers. One place I worked with tracked a noticeable drop in field failure rates directly linked to improvements in their ESD program.
Safer Workplace
This is absolutely critical, especially in industries dealing with flammable or explosive materials.
- Fire and Explosion Prevention: Controlling static electricity eliminates a common, invisible ignition source for flammable vapors, dust clouds, or other hazardous materials. This is a fundamental safety requirement in many environments.
- Personnel Safety: While typical ESD events are low energy, they can be startling and potentially cause workers to flinch or drop items, leading to secondary accidents. In specific high-voltage scenarios or near sensitive medical equipment, direct risks exist too.
Stronger Reputation and Compliance
Quality, reliability, and safety build trust with customers and partners.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Customers receiving products that work reliably from day one and last longer are more likely to be satisfied and become repeat buyers.
- Enhanced Brand Image: A reputation for high quality and dependability is a valuable competitive advantage.
- Meeting Industry Standards: Many sectors, particularly electronics, aerospace, medical, and automotive, require adherence to formal ESD control standards like ANSI/ESD S20.20 or IEC 61340-5-1. Compliance can be essential for winning contracts and operating legally.
Here’s the bottom line on why it’s worth it:
| Benefit Area | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Quality & Cost | More profit, less waste, fewer returns |
| Safety | Protects people and property |
| Reputation | Builds trust, meets industry requirements |
Good ESD control isn’t just about following rules or adding expense; it’s a strategic investment in the quality, safety, and overall success of your business.
Conclusion
In short, understanding and controlling static discharge is vital. It protects your products, ensures safety, saves money, and builds trust. Don’t underestimate the power of that tiny spark.